What makes you choose pellet instead of fossil fuel?
What is pellet?
Pellet fuel is becoming more and more important around the world, it is a suitable choice for home heating due to it’s renewable, low cost and cleaning. It is a renewable biomass product which materials are usually waste wood. Millions of people in Europe and the United States use wood pellet heating for freestanding stoves, fireplaces, furnaces and boilers. Pellets can be used in industrial applications and power generation as an alternative or supplement to coal in cogeneration projects. Wood pellets fuel can also be used in large venues such as schools and prisons. Pellets are manufactured around the world and their cross-border transactions are very active. In short, pellet fuel is a existent way of effectively converting millions of waste into energy.
Firewood, wood pellets, wood chips, wastepaper, and many other agricultural and sideline products can all be used for energy production, all of which are biomass fuels. The most striking aspect of biomass is its reproducibility. Significant particulate fuel consistency and fuel efficiency produce a small fraction of particulate emissions. Pellet burners are equipped with the lowest particulate emissions of all solid fuel burners. Properly managed by agriculture, biomass is virtually limitless and biomass prices have proved more stable than fossil fuels.

Why choose pellet?
-
Environmental protection
The main advantage of woody biomass pellets is their carbon neutrality. Plants absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen. After the plants have wilted, they release carbon dioxide during decomposition or combustion. The net increase of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is zero. In contrast, carbon dioxide released by burning fossil fuels accelerates global warming. In addition, biomass can utilize other materials that are considered discarded.
-
Convenience
Why not directly burn logs, wood chips or other biomass raw materials? One of the reasons is the moisture content. Even the moisture content of dried wood tends to be about 30%, while the moisture content of wood pellets is less than 10%. The difference is that the smoke generated by the combustion pellets is significantly reduced. Second, the pellets produce less ash, which is removed during the granulation due to soil and bark. Third, and most important, energy density. The energy density of sawdust particles is 3 times larger than that of wood chips. This drastically reduces storage requirements, delivering more fuel in a given truck space and taking up less storage space. Finally, pellet pretreatment is simple. Its uniform shape and size allow the use of smaller and simpler feeding systems and lower costs. This high density and uniform shape can be stored in a standard silo delivered by rail car delivery and truck container deliveries.
The convenience of particles is reflected in the following aspects:
- density: about 650 kg/㎡
- Can be used in furnaces and boilers
- Can be used for small and large applications
- Easy to handle, store and transport
- Improve the combustion characteristics of raw materials
-
A wide range of raw materials
Sawdust is the most common raw material used to make pellets because it does not require excessive pre-treatment before entering the sawdust pellet machine. However, there are other optional ingredients. Options include biomass waste such as wood waste (sawdust, shavings and wood peel), yard waste (grass, leaves, branches, forsythia, wisteria and shrubs), farm waste (corn cobs, corn stalks, straw stalks) .
The most common agricultural biomass used to make pellets is grass, switchgrass, thorn thistle, olive, rapeseed, sunflower and others.
Industry standard of pellet
Some countries have established their own standards, and in Europe, the European Committee for Standardization seeks to strengthen the regulation of biomass pellets.
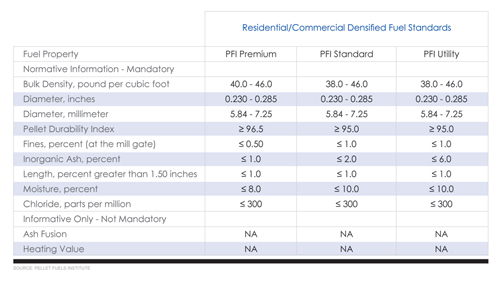
1.American standard
The U.S. solid fuel standards are set by the Pellet Fuel Association (PFI) and are voluntary. The following table lists the three types of pellet size: quality, standard and utility.
2.European Committee for Standardization (CEN)
Different European national standards are known as the European common standards for solid fuels (CEN), such as Austria, Sweden, the United Kingdom, France and Denmark. European Committee for Standardization (CEN / TC335) has developed technical specifications and test methods for solid biofuels. CEN / TS14961 covers the standards for dense solid fuels, such as pellets and briquettes. Listed below are the solid fuel standards that different countries follow, such as Austria, Sweden, the United Kingdom, France and Denmark, although these individual standards have been replaced by the so-called European Common-Use Standard for Solid Fuel (CEN).
The European Common Criteria for Solid Biofuels was created to avoid ambiguity. In the past, many European countries had their own standards. European Committee for Standardization (CEN / TC335) Preparation of solid biofuels technical specifications and test methods. Here are some CEN-based solid biofuel standards:
- Sort biomass. According to CEN ISO / TS 14961, biomass sources fall into three categories: woody, herbaceous, fruit and mixed.
- The main form of trade is solid biofuels.
- According to CEN's pelleting fuels specification.
GEMCO is a professional pellet press machine manufacture, we produce saw dust pellet machines, wood chip pellet machines and other kinds of pellet machines. Customers can customize your own pellet machine according to your material. We have professional designing team at your service. Welcome to consult at any time.




